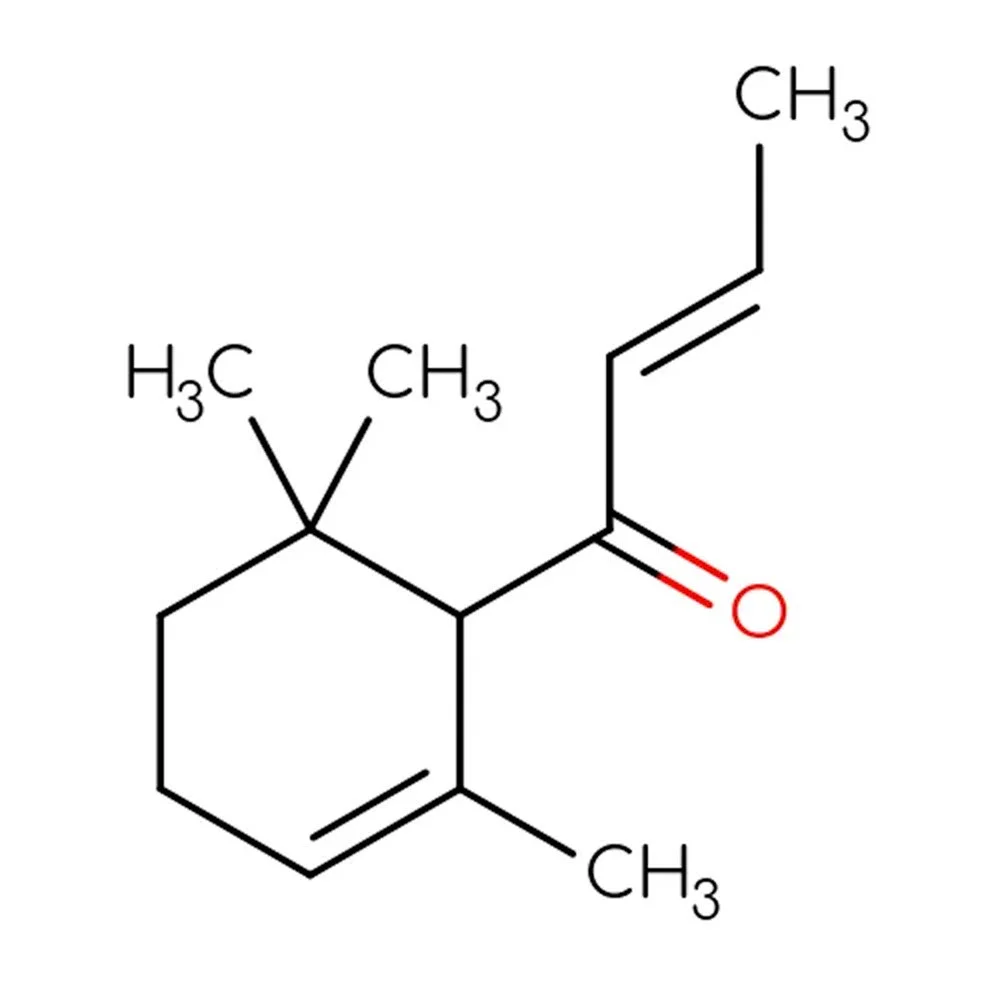
Ocimene (β-Ocimene) - Technical ingredient Overview
🔎 Chemical Name — 3,7-Dimethyl-1,3,6-octatriene
🧪 Synonyms — β-Ocimene, (E)-β-ocimene, trans-β-ocimene, p-ocimene
📂 CAS Number — 13877-91-3
📘 FEMA Number — 3539
⚖️ Molecular Weight — 136.23 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Floral, herbaceous, green, terpenic
📈 Odor Strength — Moderate to strong diffusive character
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Warm, floral, herbaceous, sweet with terpenic, green, woody, and tropical nuances; fresh with citrus-like facets
⚗️ Uses — Fine fragrance (floral compositions), flavor applications, plant defense compounds, perfumery intermediate
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellow liquid
What is Ocimene?
Ocimene is an acyclic monoterpene hydrocarbon belonging to the terpene class, characterized by three conjugated double bonds in its molecular structure (Bauer et al., 2001). The compound exists as multiple stereoisomers, with (E)-β-ocimene (trans-β-ocimene) being the most commercially significant form. As a C₁₀H₁₆ compound, ocimene consists of two isoprene units joined in a linear configuration, distinguishing it from cyclic monoterpenes like the pinenes. The molecule’s three double bonds confer high reactivity and volatility, making it both an important natural product and a useful synthetic intermediate in fragrance chemistry.
Ocimene occurs naturally in numerous essential oils and constitutes a significant component of floral scents across diverse plant species, where it functions as both an attractant for pollinators and a defense signaling molecule against herbivores (Rowe, 2005).
Historical Background
Ocimene was identified early in the study of plant volatiles and terpene chemistry, with isolation from various essential oils including bay oil (Myrcia acris), hops (Humulus lupulus), and turpentine oils throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The compound’s name derives from the genus Ocimum (basil family), where it was prominently detected.
Industrial synthesis of ocimene developed alongside advances in terpene chemistry during the mid-20th century. The primary commercial production method involves pyrolytic cleavage of α-pinene through thermal rearrangement, a process discovered as turpentine chemistry matured (Bauer et al., 2001). When α-pinene undergoes controlled thermal decomposition (pyrolysis), the bicyclic structure opens to yield a mixture of ocimene and alloocimene isomers. This transformation established ocimene as an accessible material for industrial applications, particularly as both essential oils and turpentine derivatives became widely available as starting materials.
Alternative synthetic pathways include dehydration and rearrangement of linalool under specific catalyst conditions, though pyrolysis remains the dominant industrial method.
Olfactory Profile
Scent Family
Floral, herbaceous, terpenic, green
Main Descriptors
Primary: Warm, floral, herbaceous, sweet
Secondary: Terpenic, green, woody, tropical
Tertiary: Fresh citrus-lime notes, fruity facets, wet cloth character
Intensity
Moderate to strong diffusive character. Ocimene demonstrates substantial volatility and diffusion capacity typical of acyclic monoterpenes, contributing significantly to headspace aromatics even at low concentrations.
Tenacity
Low to moderate persistence. As a highly volatile monoterpene with three double bonds, ocimene evaporates rapidly, functioning primarily as a top note material. The compound’s lack of structural complexity limits its substantivity on substrates.
Volatility
Extremely high volatility (boiling point 65-66°C at 13 mmHg). Functions exclusively as a top note material. The conjugated triene structure and low molecular weight result in immediate evaporation upon exposure to air, making ocimene ideal for providing fresh, diffusive opening notes in fragrance compositions.
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Ocimene serves primarily as a floral modifier and fresh top note contributor in perfumery compositions. The material finds particular utility in creating neroli effects, eau de cologne freshness, and herbaceous-floral accords. Notable uses include:
Floral Compositions: Enhances lily-of-the-valley (muguet), orchid, and white floral bases with natural green-floral character
Citrus Accords: Contributes authentic fresh citrus-lime nuances and licorice-anise facets
Oriental Fragrances: Adds diffusive freshness to opoponax and herbal-oriental bases
Fresh Topnotes: Provides immediate impact and natural diffusion in modern eau de cologne structures
The compound’s characteristic warm-herbaceous profile makes it especially valuable for compositions requiring natural botanical authenticity and uplifting, diffusive freshness.
Performance in Formula
Ocimene exhibits typical behavior of highly unsaturated acyclic terpenes: rapid evaporation, high diffusion, and susceptibility to oxidation. Formulators must stabilize ocimene-containing compositions with antioxidants (BHT commonly used) to prevent autoxidation and off-note development. The material blends effectively with other monoterpenes, citrus oils, and floral absolutes, though its fugacity limits its contribution to base and heart notes. Best performance achieved in alcohol-based compositions where its volatility enhances opening impact.
Industrial & Technical Uses
Beyond perfumery, ocimene serves as a flavoring agent (FEMA 3539) contributing green, woody, and tropical notes to food applications at typical use levels of 40 ppm. The compound functions as an intermediate for synthesizing other terpenoid derivatives and fragrance materials. Notably, ocimene plays crucial ecological roles as a volatile plant signaling compound involved in plant defense mechanisms, acting as both an insect attractant for beneficial species and a deterrent for herbivorous pests. This dual functionality has generated research interest in agricultural applications for biological pest control.
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status: No restrictions under IFRA Amendment 51 for standard fragrance applications (https://ifrafragrance.org)
EU Cosmetics Regulation: Compliant with EU Regulation 1223/2009 for cosmetic use
FEMA Status: FEMA 3539 (approved flavor ingredient); meets JECFA purity specifications
Additional Classifications: Flavis Number 1.018, EC Number 237-641-2, FDA 21 CFR 172.515
Toxicology: Generally recognized as safe for intended uses. Material classified as Flammable Liquid Category 3 and Self-heating Category 2. Handle with appropriate precautions regarding reactivity and oxidation potential. No allergen concerns under current EU regulations.
References
Bauer, K., Garbe, D., & Surburg, H. (2001). Common fragrance and flavor materials: Preparation, properties and uses(4th ed.). Wiley-VCH.
International Fragrance Association. (2023). IFRA Standards Amendment 51. https://ifrafragrance.org
Rowe, D. J. (Ed.). (2005). Chemistry and technology of flavors and fragrances. Blackwell Publishing.
Zviely, M. (2013). Ocimene—A versatile floral ingredient. Perfumer & Flavorist, 38(1), 42-47.