Technical Ingredient Overview
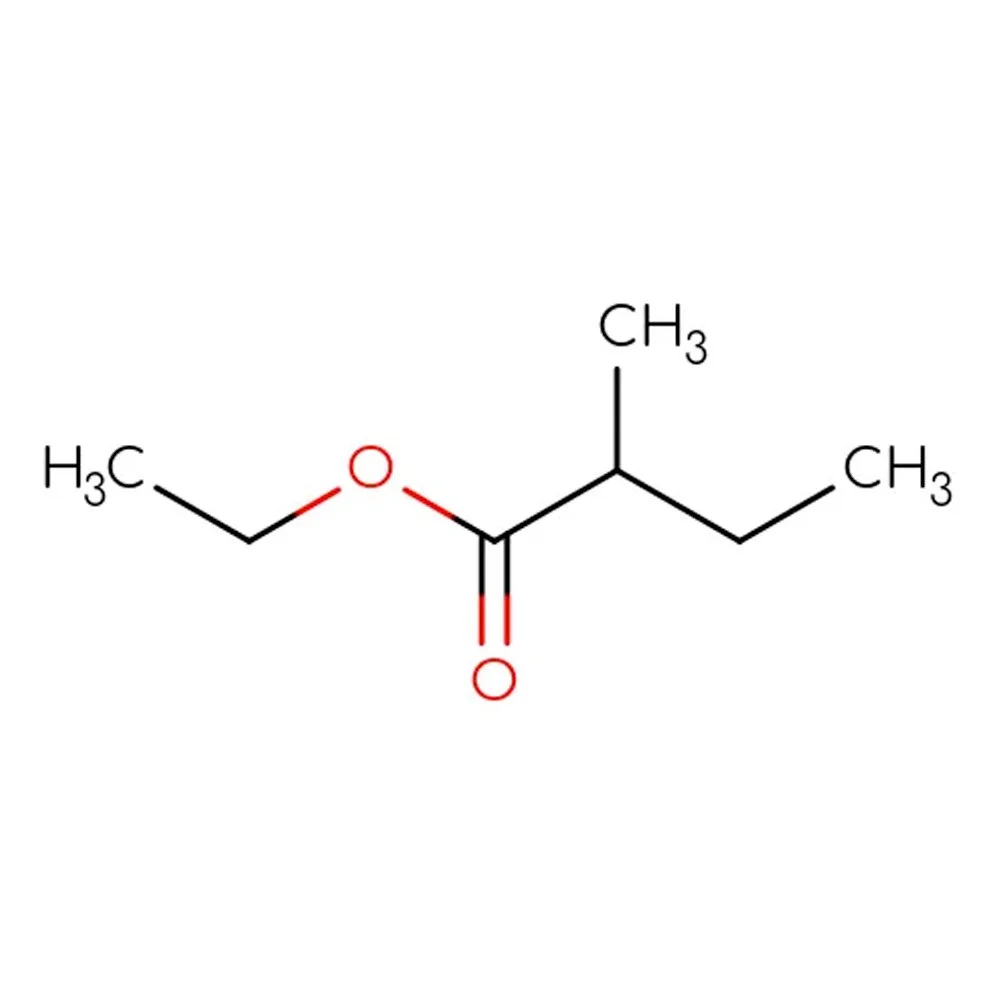
🔎 Chemical Name — Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate
🧪 Synonyms — Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate; Butanoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester; Ethyl α-methylbutyrate
📂 CAS Number — 7452-79-1
📘 FEMA Number — 2443
🧬 Molecular Formula — C7H14O2
⚖️ Molecular Weight — 130.19 g/mol
📝 Odor Type — Fruity ester, green-fruity
📈 Odor Strength — Strong, radiant top note with high diffusion
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Green-apple, pineapple skin, unripe plum peel, ethereal, diffusive fruity-green with apple and peach nuances
⚗️ Uses — Flavoring agent (beverages, confectionery); fragrance modifier in fruity-floral compositions; top-note enhancer
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellow liquid with characteristic fruity odor.
What is Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate? Understanding This Essential Fruity Ester
Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate (ethyl 2-methylbutyrate) is a premium fruity ester widely used in perfumery and fragrance creation for its distinctive green-apple and pineapple aroma. This synthetic aromatic compound, produced through acid-catalyzed esterification of 2-methylbutanoic acid with ethanol, serves as a cornerstone ingredient in modern fruity-floral fragrance compositions and natural fruit flavor applications.
Found naturally in apples, plums, pineapples, and oranges, ethyl 2-methylbutanoate delivers the fresh, green-fruity character that perfumers and fragrance chemists rely on for creating authentic fruit accords. Its unique branched aliphatic structure distinguishes it from linear esters, providing the characteristic unripe fruit and apple-skin notes that have made it indispensable in contemporary fragrance formulation.
Historical Background: From Fruit Research to Modern Perfumery
The discovery and characterization of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate emerged from pioneering fruit aroma research conducted during the mid-20th century. When gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) techniques revolutionized analytical chemistry in the 1950s and 1960s, researchers could finally identify the precise volatile organic compounds responsible for natural fruit fragrances and flavors.
Commercial synthesis and widespread adoption in the fragrance and flavor industries expanded dramatically during the 1960s-1970s, as analytical advances revealed ethyl 2-methylbutanoate’s critical importance in creating authentic green-apple and tropical fruit accords. Fragrance houses like Givaudan, Firmenich, and IFF began incorporating this versatile ester into their aromatic palettes, recognizing its unique ability to bridge fresh top notes with fruity heart compositions.
The compound’s inclusion in the FEMA GRAS list as number 2443 cemented its commercial significance, enabling widespread use across both perfumery applications and food flavoring systems. Today, ethyl 2-methylbutanoate remains a fundamental building block for perfumers creating everything from fresh colognes to complex fruity-floral masterpieces.
Olfactory Profile: Mastering Green-Fruity Fragrance Notes
Understanding the complete olfactory profile of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate is essential for perfumers and fragrance enthusiasts working with fruity compositions:
Scent Family: Fruity esters (aliphatic ester subgroup) - the cornerstone of modern green-fruity accords
Primary Descriptors: Crisp green-apple, fresh pineapple skin, unripe plum peel, ethereal fruitiness with distinctive apple and peach nuances
Olfactory Intensity: High-impact top note with exceptional diffusion and immediate recognition
Fragrance Longevity: Moderate persistence on fragrance strips (30-45 minutes) with limited substantivity requiring fixative support
Volatility Characteristics: High volatility (boiling point 129°C, vapor pressure 7.4657 hPa at 20°C) making it ideal for sparkling top note effects
Fixative Properties: Limited fixative strength; functions primarily as radiant top-note enhancer requiring support from musks, ambergris, or resinous fixatives
The exceptional diffusion characteristics of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate make it invaluable for creating immediate olfactory impact in fragrance compositions. Perfumers particularly value its transparency and naturalness in summery applications, where its green-fruity character provides authentic fruit recognition without synthetic artificiality. This makes it essential for both niche perfumery and commercial fragrance development targeting fresh, youthful, and energetic fragrance profiles.
Applications in Fine Fragrance: Creating Perfect Fruity Compositions
Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate represents an indispensable tool in the modern perfumer’s palette, excelling in multiple fragrance categories and applications. Its versatility in creating authentic fruity-green accords makes it essential for both artisanal perfumery and commercial fragrance development.
Essential Fragrance Applications:
Fruity-Floral Perfumes: Provides signature crisp green-apple opening notes that transition beautifully into floral heart compositions
Fresh & Marine Fragrances: Contributes sparkling, aquatic-compatible fruitiness without heaviness
Youth-Oriented & Contemporary Scents: Essential for modern fruity profiles targeting millennial and Gen-Z consumers
Unisex & Gender-Neutral Fragrances: Delivers clean fruitiness appealing across gender boundaries
Functional & Lifestyle Fragrances: Enhances perception of freshness, cleanliness, and vitality in personal care applications
Expert Blending Combinations: The ingredient demonstrates exceptional synergy with complementary materials including ethyl butyrate (pear-like fruitiness), γ-undecalactone (creamy peach), and various aldehydes for sparkling effects. Master perfumers frequently combine ethyl 2-methylbutanoate with lily-of-the-valley, freesia, and light rose facets, where its green aspects enhance rather than compete with delicate floral nuances.
Commercial Success Stories: While specific fragrance formulations remain proprietary, industry sources confirm ethyl 2-methylbutanoate’s presence in numerous successful commercial launches across categories ranging from celebrity fragrances to niche artisanal creations, particularly those emphasizing natural fruitiness and contemporary appeal.
Performance in Fragrance Formulation: Technical Guidelines for Perfumers
Understanding the formulation behavior of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate is crucial for achieving optimal performance in finished fragrance compositions. This versatile ester offers excellent compatibility with standard perfumery materials while requiring specific technical considerations for maximum effectiveness.
Critical Formulation Parameters:
Recommended Usage Levels: 0.1-2% in fine fragrance applications, with optimal impact typically achieved at 0.5-1%
Solubility Profile: Excellent miscibility with ethanol, dipropylene glycol, and benzyl benzoate; limited water solubility requires careful consideration in aqueous applications
Chemical Stability: Good stability under normal storage conditions; sensitive to strong bases and acids which can cause hydrolysis
Blending Compatibility: Outstanding harmony with fruity esters, aldehydic materials, and light aromatic compounds
Enhancement Properties: Significantly improves projection and diffusion of light top notes while maintaining transparency
Technical Performance Considerations: The molecule’s high volatility characteristics necessitate strategic formulation approaches to prevent rapid dissipation. Professional perfumers often employ encapsulation techniques, careful fixative balance, or controlled-release technologies to ensure sustained performance throughout the fragrance evolution. The ingredient’s tendency toward rapid evaporation can be advantageous for creating dramatic opening effects but requires expert handling to maintain presence in the composition’s development.
Quality Control Standards: For consistent performance, ethyl 2-methylbutanoate should be stored in cool, dark conditions away from heat and light sources. Purity specifications typically require >95% chemical purity with minimal aldehyde contamination to prevent off-notes in finished compositions.
Industrial & Technical Applications: Beyond Fine Fragrance
The commercial applications of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate extend far beyond traditional perfumery, encompassing food and beverage flavoring, cosmetic applications, and specialized industrial uses. Its GRAS approval (FEMA 2443) enables widespread utilization across consumer product categories.
Food & Beverage Flavoring Applications:
Fruit-Flavored Beverages: Essential for authentic apple, plum, and pineapple flavor profiles in soft drinks, juices, and alcoholic beverages
Confectionery & Desserts: Provides natural fruit character in candies, ice cream, yogurt, and baked goods
Snack Foods & Processed Products: Enhances fruit flavoring in cereals, granola bars, and convenience foods
Maximum Usage Levels: Up to 10 ppm in flavor applications, with typical usage ranging 1-5 ppm for optimal effect
Cosmetic & Personal Care Applications:
Body Care Products: Shampoos, body washes, and lotions targeting fresh, fruity positioning
Skin Care Formulations: Anti-aging and brightening products utilizing apple-association marketing
Hair Care Systems: Color-protecting and volumizing products emphasizing freshness and vitality
Functional Fragrancing: Air care products, household cleaners, and fabric care applications
Specialized Technical Uses:
Aromatherapy Products: Natural-smelling stress relief and energizing formulations
Automotive & Industrial: Air fresheners and environmental fragrance systems
Textile Applications: Fabric softeners and scent-release fiber treatments
The ingredient’s versatility across applications stems from its excellent safety profile, regulatory acceptance, and consumer appeal, making it valuable for product developers across multiple industries seeking authentic fruity character.
Regulatory & Safety Profile: Comprehensive Compliance Information
The regulatory status of ethyl 2-methylbutanoate reflects its excellent safety profile and widespread acceptance across global markets. Understanding these regulatory aspects is essential for formulators working in international markets and seeking compliant ingredient solutions.
International Fragrance Regulations:
IFRA Guidelines: No specific restrictions through the 51st Amendment; classified under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines for standard fragrance applications
EU Cosmetic Regulation: Fully permitted without restriction under Annex VII; not classified as CMR (Carcinogenic, Mutagenic, Reprotoxic) substance
Allergen Status: Not recognized as a fragrance allergen under EU or US regulations; no mandatory labeling requirements
Food Safety & GRAS Status:
FEMA GRAS Classification: Approved as Generally Recognized As Safe under FEMA number 2443 for food and beverage applications
FDA Status: Accepted for food use with established safety parameters and maximum usage levels
Global Food Approval: Recognized in major markets including EU, Canada, Australia, and Japan
Toxicology & Safety Data:
Acute Toxicity: LD₅₀ > 2000 mg/kg (oral, rat) - classified as practically non-toxic
Skin Sensitization: Minimal sensitization potential at typical use concentrations in fragrance applications
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable ester structure with favorable environmental profile
Occupational Safety: Standard precautions for organic esters apply; no special handling requirements beyond good laboratory practices
GHS Classification & Labeling: Under the Globally Harmonized System, ethyl 2-methylbutanoate is generally classified as non-hazardous under normal use conditions, requiring only standard safety precautions typical for organic ester materials used in fragrance and flavor applications.
Environmental Impact & Sustainability: Responsible Fragrance Chemistry
Modern fragrance development increasingly emphasizes environmental responsibility and sustainable practices. Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate offers several advantages from an environmental and sustainability perspective, making it an attractive choice for eco-conscious formulators and brands.
Environmental Advantages:
Biodegradability: The ester structure ensures complete biodegradation under standard environmental conditions, preventing bioaccumulation
Natural Occurrence: Found naturally in common fruits, indicating environmental compatibility and biological integration
Low Environmental Impact: Minimal ecological footprint during production and use phases
Sustainable Production Pathways:
Renewable Feedstocks: Synthesis from renewable ethanol and bio-derived methylbutanoic acid reduces dependency on fossil fuel sources
Green Chemistry: Modern production methods employ environmentally friendly catalysts and minimize waste generation
Energy Efficiency: Optimized synthesis routes reduce energy consumption compared to traditional chemical processes
Responsible Sourcing & Supply Chain: Leading suppliers increasingly offer ethyl 2-methylbutanoate produced through sustainable methods, including renewable feedstock utilization and carbon-neutral production facilities. This enables fragrance brands to meet sustainability targets while maintaining product performance and consumer appeal.
Circular Economy Integration: The compound’s biodegradable nature and renewable production potential make it well-suited for circular economy principles in fragrance development, supporting brands seeking comprehensive sustainability credentials across their ingredient portfolios.
Comparative Analysis: Ethyl 2-Methyl Butyrate vs Related Fruity Esters
Understanding how ethyl 2-methylbutanoate compares to related fruity esters helps perfumers make informed ingredient selections and optimize fragrance compositions. This comparative analysis highlights key differences and synergistic opportunities.
vs. Ethyl Butyrate (CAS 105-54-4):
Olfactory Difference: Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate provides greener, more apple-like character while ethyl butyrate offers classic pineapple-banana fruitiness
Volatility: Similar evaporation rates but different diffusion profiles
Blending: Excellent synergy when combined in 2:1 or 3:1 ratios for complex fruit accords
vs. Isoamyl Acetate (CAS 123-92-2):
Character Distinction: Less banana-like, more sophisticated green-fruit profile
Intensity: More subtle and refined compared to isoamyl acetate’s bold banana character
Application: Better suited for elegant fruity-florals rather than gourmand compositions
vs. Hexyl Acetate (CAS 142-92-7):
Fruit Type: Apple-pineapple versus pear-apple differentiation
Tenacity: Similar volatility but different persistence curves
Compatibility: Both excellent in fresh compositions but serve different olfactory roles
Strategic Blending Recommendations: Master perfumers frequently combine ethyl 2-methylbutanoate with complementary esters to create sophisticated fruit accords that transcend single-ingredient limitations. Popular combinations include pairing with ethyl heptanoate for tropical complexity or with methyl anthranilate for grape-apple nuances.
Sources:
Arctander, S. (1969). Perfume and Flavor Materials of Natural Origin. Elizabeth, NJ: Arctander.
CymitQuimica. (2019). CAS 7452-79-1: Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate. Retrieved from https://cymitquimica.com/cas/7452-79-1/
European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). (2025). Registered Substances: Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate. Retrieved from https://echa.europa.eu/
Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association (FEMA). (2025). FEMA GRAS Listing: Ethyl 2-Methylbutyrate (FEMA No. 2443). Washington, DC: FEMA.
The Fragrance Conservatory. (2025). Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate. Retrieved from https://fragranceconservatory.com/ingredient/ethyl-2-methylbutyrate
Givaudan. (2025). Ethyl Methyl-2-Butyrate [Technical data sheet]. Vernier, Switzerland: Givaudan.
International Fragrance Association (IFRA). (2025). IFRA Standards 51st Amendment. Geneva, Switzerland: IFRA.
PubChem. (2025). Ethyl 2-methylbutyrate, CID 24020. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24020
Sell, C. S. (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances: From Perfumer to Consumer (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Sigma-Aldrich. (2025). Safety Data Sheet: Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate. St. Louis, MO: Merck KGaA.