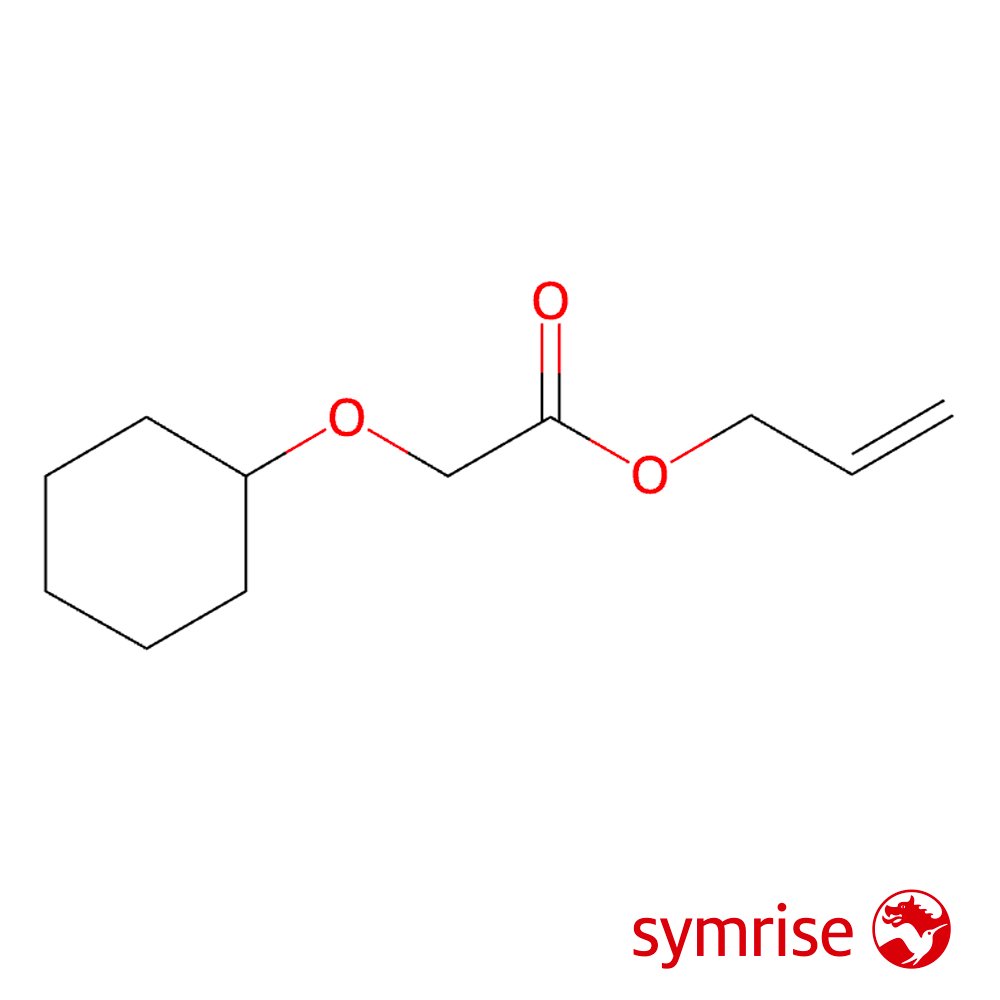
Technical Ingredient Overview
🏭 Manufacturer — Symrise (originally developed by Dragoco S.A.)
🔎 Chemical Name — Allyl (cyclohexyloxy)acetate
🧪 Synonyms — Acetic acid, (cyclohexyloxy)-, 2-propenyl ester; Allyl cyclohexyloxyacetate; Cyclogalbanat; Cyclogalbaniff; Isoananat; Galbanum oxyacetate (Api et al., 2015)
📂 CAS Number — 68901-15-5
📘 FEMA Number — Not assigned (not approved for flavor use)
⚖️ Molecular Weight — 198.26 g/mol (Api et al., 2015)
📝 Odor Type — Green → Fruity → Herbal
📈 Odor Strength — Medium to strong; persistent with moderate volatility
👃🏼 Odor Profile — Crisp green with pronounced pineapple-like fruitiness, herbal galbanum undertones, slightly resinous and balsamic nuances. The olfactory character bridges natural galbanum resin complexity with bright tropical fruit accents, creating a hybrid green-fruity signature that softens traditional harsh green notes while maintaining verdant freshness.
⚗️ Uses — Primarily utilized in fine fragrance compositions to enhance floral-fruity accords, particularly in fougère, chypre, and modern green-floral structures. Functions as a middle-note enhancer supporting transitions from citrus or herbal top notes to heavier floral or woody bases. Adds naturalistic brightness and complexity to dense compositions. Typical usage concentration: 0.1–5% in fragrance compounds (Api et al., 2015).
🧴 Appearance — Colorless to pale yellowish clear liquid with moderate volatility. Specific gravity: 1.012–1.020 @ 25°C. Flash point: >100°C (Api et al., 2015).
What is Cyclogalbanate?
Cyclogalbanate, chemically designated as allyl (cyclohexyloxy)acetate (CAS 68901-15-5), is a synthetic aliphatic ester belonging to the allyl ester class of fragrance materials (Api et al., 2015). The molecule features a cyclohexyloxy moiety attached to an acetate group, which is further esterified with an allyl alcohol component, creating a molecular architecture of C₁₁H₁₈O₃.
This synthetic aroma chemical was specifically engineered to replicate and extend the olfactory profile of natural galbanum resin (Ferula galbaniflua) while incorporating fruity pineapple-like characteristics absent in the natural material. The result is a versatile green-fruity building block that offers perfumers enhanced formulation stability, cost-effectiveness, and creative flexibility compared to natural galbanum extracts.
Structurally, Cyclogalbanate's allyl ester configuration contributes to its characteristic volatility profile and reactivity behavior in fragrance compositions. The cyclohexyloxy substituent provides lipophilic character (log Kow = 2.72), facilitating substantivity on skin and textiles while modulating the material's overall olfactory intensity (Api et al., 2015).
Historical Background
Cyclogalbanate was developed during an innovative period of aromatic chemistry research at Dragoco S.A. in West Germany during the early to mid-1980s (1982–1986). The principal researchers credited with its invention were Hans Warnecke and Ernst Brunke, who were part of Dragoco's synthetic aroma chemicals division focused on creating sustainable alternatives to scarce and expensive natural raw materials.
The development objective was twofold: to create molecules capable of replicating the complex green-resinous character of natural galbanum resin while providing superior technical performance characteristics including photostability, batch-to-batch consistency, regulatory compliance, and cost predictability. This period coincided with broader industry trends toward "nature-identical" and "nature-inspired" synthetics driven by supply chain concerns and sustainability considerations.
Dragoco S.A. was subsequently acquired and integrated into Symrise AG following the 2003 merger between Dragoco and Haarmann & Reimer, both historic German fragrance houses with roots extending to the 19th century. Symrise has continued to manufacture and market Cyclogalbanate as part of its extensive aroma chemicals portfolio.
The molecule represents a successful example of targeted molecular design in fragrance chemistry, where specific structural modifications to the ester backbone were employed to achieve desired olfactory characteristics. Subsequent research by fragrance chemists including Philip Kraft has explored Cyclogalbanate's structural compatibility with aldehydes, ionones, and other synthetic florals, confirming its utility as a modular green-building block in contemporary perfumery (Kraft, various publications).
Olfactory Profile
Scent Family
Cyclogalbanate is classified within the Green fragrance family, with significant Fruity and Herbal subfacets. It occupies a specialized position in the olfactory spectrum, bridging crisp vegetative green notes characteristic of galbanum resin with bright tropical fruit nuances reminiscent of pineapple and green apple.
Main Descriptors
The primary olfactory characteristics include:
Green: Fresh, vegetative, leafy character with crisp natural quality
Fruity: Pronounced pineapple and green apple aspects providing brightness and approachability
Herbal: Subtle aromatic undertones with galbanum-like resinous depth
Balsamic: Light resinous background adding complexity and naturalness
Fresh: Clean, uplifting quality without harsh or sharp edges
The overall effect is a softened, accessible interpretation of natural galbanum that maintains the essential green character while introducing fruity sweetness that broadens application versatility.
Intensity
Cyclogalbanate exhibits medium to strong odor intensity. The material possesses sufficient diffusive power to impact compositions at low concentrations (0.1–1%) while remaining balanced and harmonious at higher usage levels (up to 5%). The intensity is perceptible but not overwhelming, allowing for nuanced layering with other fragrance components.
Tenacity
The material demonstrates good tenacity with moderate persistence in fragrance applications. As a middle-note enhancer, Cyclogalbanate exhibits sustained presence throughout the heart phase of fragrance development, typically persisting for 4–8 hours on skin depending on formulation context and concentration. The allyl ester structure contributes to substantivity while avoiding excessive volatility that would relegate the material to pure top-note character.
Volatility
Cyclogalbanate is characterized by moderate volatility with a vapor pressure of 0.021 mm Hg @ 25°C and boiling point of 254.86°C (calculated) (Api et al., 2015). This physical profile positions the material primarily as a middle notecomponent with some top-note lift, creating bridging functionality between volatile citrus/herbal introductions and substantive base note foundations. The allyl group provides initial diffusion, while the cyclohexyloxy-acetate backbone ensures sustained presence.
Fixative Role
While not classified as a traditional base-note fixative, Cyclogalbanate contributes moderate fixative influence within middle-note structures. The material's lipophilic character (log Kow = 2.72) and molecular weight (198.26 g/mol) provide sufficient substantivity to support and extend the longevity of more volatile green and fruity components. It functions as a "green fixative" within specific accord contexts, particularly in fougère and chypre structures where it anchors herbaceous and fruity-floral elements.
Applications in Fine Fragrance
Cyclogalbanate serves multiple strategic roles in modern perfumery compositions:
Fragrance Structure Enhancement
The material functions primarily as a middle-note enhancer that supports architectural transitions within fragrance pyramids. It effectively bridges volatile citrus, herbal, or aromatic top notes to more substantive floral, woody, or ambery base notes, creating smooth olfactory evolution without abrupt character shifts.
Accord Development
Cyclogalbanate demonstrates particular effectiveness in several classical and contemporary accord types:
Fougère Fragrances: Harmonizes seamlessly with lavender, coumarin, oakmoss, and geranium to create sophisticated aromatic-green frameworks. The fruity aspect softens potential harshness from aromatic herbs while maintaining essential masculine freshness.
Chypre Compositions: Enhances the critical green-woody interplay characteristic of chypre structures, working synergistically with citrus bergamot introductions, labdanum-patchouli-oakmoss bases, and rose-jasmine florals. Provides contemporary brightness to classic formulations.
Floral-Fruity Accords: Elevates apple, pineapple, pear, and tropical fruit notes while supporting jasmine, gardenia, lily, and muguet florals. The green facet prevents cloying sweetness and adds dimensional complexity.
Green-Floral Compositions: Serves as central structural component in modern green-floral concepts, providing naturalistic depth and fruity accessibility that broadens consumer appeal beyond traditional niche green fragrances.
Ingredient Pairing Behavior
Cyclogalbanate exhibits favorable blending characteristics with numerous fragrance materials:
Synthetics: Balances aldehydes (particularly C-10, C-11, C-12), synthetic jasmines (Hedione, methyl dihydrojasmonate), ionones (alpha and beta), and modern musks
Naturals: Complements bergamot, lavender absolute, clary sage, oakmoss, patchouli, vetiver, and rose oils
Specialty Molecules: Works effectively with Ambroxan, Iso E Super, Cashmeran, and Galaxolide family musks
Functional Fragrance Applications
Beyond fine fragrance, Cyclogalbanate finds application in functional fragrance categories where green-fresh profiles are desired:
Personal Care: Shampoos, conditioners, shower gels, and body lotions with herbal-fresh positioning
Home Care: Fabric softeners, detergents, and surface cleaners requiring natural green character
Air Care: Room sprays and aerosol products leveraging fresh-fruity appeal
The material's moderate volatility and substantivity make it suitable for leave-on and rinse-off applications, though usage must comply with IFRA standards (see Regulatory section).
Performance in Formula
Behavior in Blends
Cyclogalbanate demonstrates predictable and stable behavior in fragrance formulations across multiple solvent systems including ethanol, dipropylene glycol (DPG), isopropyl myristate (IPM), and various cosmetic bases. The material exhibits good solubility in alcoholic and oil-based media, facilitating incorporation into diverse product matrices.
The allyl ester functionality requires formulation awareness regarding potential reactivity. While generally stable under normal storage conditions (sealed, cool, dark), prolonged exposure to strong acids, bases, or oxidizing agents should be avoided. The IFRA standard specifying maximum 0.1% free allyl alcohol content addresses potential irritation concerns (see Regulatory section).
Impact on Overall Composition
Within fragrance compositions, Cyclogalbanate contributes multiple functional benefits:
Brightness Enhancement: Adds luminosity and lift to compositions that might otherwise present as heavy or dense
Natural Complexity: Introduces multifaceted green-fruity character that mimics natural material complexity
Transition Smoothing: Facilitates seamless evolution between fragrance phases, reducing perceptual "jumps" or discontinuities
Cost Efficiency: Provides high-impact olfactory contribution at relatively low usage concentrations, optimizing formulation economics
Stability Contribution: Offers superior photostability and oxidative resistance compared to many natural green materials
The material's moderate strength allows perfumers to control intensity through concentration adjustment, enabling both subtle background greenness and pronounced fruity-green character depending on creative intent.
Industrial & Technical Uses
Non-Fragrance Applications
Cyclogalbanate is classified exclusively as a fragrance ingredient and is not approved for flavor applications. The material does not possess FEMA GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status and is not listed in the Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients. The Volatile Compounds in Food (VCF) database confirms that allyl (cyclohexyloxy)acetate does not occur naturally in food products (Api et al., 2015).
Regulatory & Safety Overview
IFRA Status
Cyclogalbanate is regulated under the IFRA Standards (International Fragrance Association) with specific restrictions. According to IFRA Amendment 51 (latest available documentation as of 2025), the material carries the following specification:
Use only when the level of free allyl alcohol is less than 0.1% (IFRA, based on the delayed irritant potential of allyl alcohol as documented in Food and Chemical Toxicology 15, 611, 1977).
This standard applies across all product categories and represents a specification requirement rather than a concentration restriction. Compliance is verified through analytical testing by manufacturers to ensure allyl alcohol impurity levels remain below the threshold.
Official IFRA documentation: https://ifrafragrance.org/safe-use/library
EU Cosmetics Regulation
Cyclogalbanate (CAS 68901-15-5) is permitted for use in cosmetic products within the European Union under Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 on cosmetic products, subject to compliance with general safety requirements and IFRA standards. The material is not listed on Annex II (prohibited substances) or Annex III (restricted substances) of the EU Cosmetics Regulation.
As an established fragrance ingredient, Cyclogalbanate is covered under the general provisions for fragrance compounds, which must comply with IFRA standards and undergo safety assessment under the EU Cosmetics Regulation framework.
FEMA Status
Cyclogalbanate is NOT approved for use as a flavoring substance. The material does not appear in the FEMA (Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association) GRAS database and has not undergone evaluation for food contact or ingestion safety. All applications are restricted to external-use fragrance products only.
GHS Classification
Under the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), Cyclogalbanate exhibits the following classification profile based on available toxicological data:
Not classified as hazardous under standard use conditions
Flash point >100°C (not classified as flammable liquid)
Not classified for acute toxicity (dermal or oral routes)
Not classified for skin sensitization based on weight-of-evidence assessment
Exhibits irritant potential requiring specification control (free allyl alcohol <0.1%)
Specific hazard classifications may vary by manufacturer SDS (Safety Data Sheet) and regional regulatory interpretation. Users should consult current supplier documentation for detailed hazard communication information.
Toxicology Summary
Comprehensive safety assessment of Cyclogalbanate has been conducted by the Research Institute for Fragrance Materials (RIFM) and published in peer-reviewed literature:
Key Toxicological Findings (Api et al., 2015):
Genotoxicity: Not genotoxic in bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) with or without metabolic activation. Read-across analog demonstrated non-clastogenic activity in in vivo micronucleus test.
Repeated Dose Toxicity: NOAEL (No Observed Adverse Effect Level) established at 7.5 mg/kg/day based on gavage reproduction dosage-range finding study in rats using read-across analog (allyl cyclohexanepropionate). Margin of Exposure (MOE) = 441, exceeding the acceptable threshold of >100.
Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity: NOAEL = 75 mg/kg/day based on read-across data. MOE = 4,412. No evidence of developmental toxicity or reproductive effects at anticipated human exposure levels.
Skin Sensitization: While chemical structure suggests potential protein reactivity, weight-of-evidence assessment including local lymph node assay, guinea pig maximization tests, and human repeated insult patch tests (HRIPT) indicates the material is not a sensitization concern under normal use conditions. Positive LLNA responses attributed to irritant rather than allergenic mechanisms.
Phototoxicity/Photoallergenicity: Not phototoxic or photoallergenic based on UV absorption spectra analysis. Molar absorption coefficient below benchmark for phototoxic concern.
Respiratory Toxicity: Inhalation exposure below Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) for Cramer Class III substances. Combined inhalation exposure = 0.059 mg/day, well below TTC limit of 0.47 mg/day.
Environmental Safety: Not classified as Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (PBT) or very Persistent and very Bioaccumulative (vPvB) under IFRA Environmental Standards. Risk Quotient (PEC/PNEC) <1 for aquatic environments in North America and Europe.
RIFM Safety Assessment: The RIFM Expert Panel concluded that "this material is safe under the limits described in this safety assessment" (Api et al., 2015). The comprehensive evaluation supports safe use in fragrance applications at reported volumes and concentrations.
Reference: Complete toxicological assessment available at: https://fragrancematerialsafetyresource.elsevier.com/
REACH Registration
Cyclogalbanate (CAS 68901-15-5) was pre-registered under the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation for the 2010 deadline. As of January 2025, no complete registration dossier is publicly available through the ECHA (European Chemicals Agency) database, suggesting registration under a consortium or private dossier arrangement typical for fragrance materials with limited tonnage bands (Api et al., 2015).
Sources
Api, A. M., Belsito, D., Bhatia, S., Bruze, M., Calow, P., Dagli, M. L., Dekant, W., Fryer, A. D., Kromidas, L., La Cava, S., Lalko, J. F., Lapczynski, A., Liebler, D. C., Miyachi, Y., Politano, V. T., Ritacco, G., Salvito, D., Shen, J., Schultz, T. W., ... Wilcox, D. K. (2015). RIFM fragrance ingredient safety assessment, allyl (cyclohexyloxy)acetate, CAS registry number 68901-15-5. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 82(Suppl.), S59–S65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.03.016
Arctander, S. (1969). Perfume and flavor chemicals (aroma chemicals). Allured Publishing Corporation.
Kraft, P., & Bajgrowicz, J. A. (2006). Fragrance chemistry. In C. Sell (Ed.), The chemistry of fragrances: From perfumer to consumer (2nd ed., pp. 73–143). Royal Society of Chemistry.
Sell, C. S. (2006). The chemistry of fragrances: From perfumer to consumer (2nd ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry.
Symrise AG. (n.d.). Cyclogalbanate technical data sheet